Problem 59

By Supreme2023-03-16
Problem Statement :
Write a program to write a string in file.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
//59. Write a program to write a string in file
printf("\tWrite String In File\n");
printf("==========================================\n");
char str[100];
printf("\nEnter A String: ");
gets(str);
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("example.txt", "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("Error Opening File!\n");
return 1;
}
fprintf(fp, "%s", str);
fclose(fp);
printf("\n------------------------------------------\n");
printf("String Written To File Successfully!\n");
printf("------------------------------------------\n");
return 0;
}
Description :
- This program is used to write a string in a file using the C programming language.
- The program starts with the
mainfunction. - The program prints out some information for the user using
printf. - It declares a character array called
strwith a size of 100. - It prompts the user to enter a string using
printfandgets, which reads a line of text from the standard input and stores it in thestrarray. - The program declares a file pointer called
fpand initializes it toNULL. - It opens the file "example.txt" in write mode using the
fopenfunction and assigns the file pointerfpto the opened file. - It checks if the file pointer
fpis NULL, indicating that the file failed to open. If it is NULL, it prints an error message and returns a value of 1 to indicate an error has occurred. - If the file opened successfully, the program writes the contents of the
strarray to the file using thefprintffunction. - It closes the file using the
fclosefunction. - It prints out a success message using
printfand returns a value of 0 to indicate the program ran successfully.
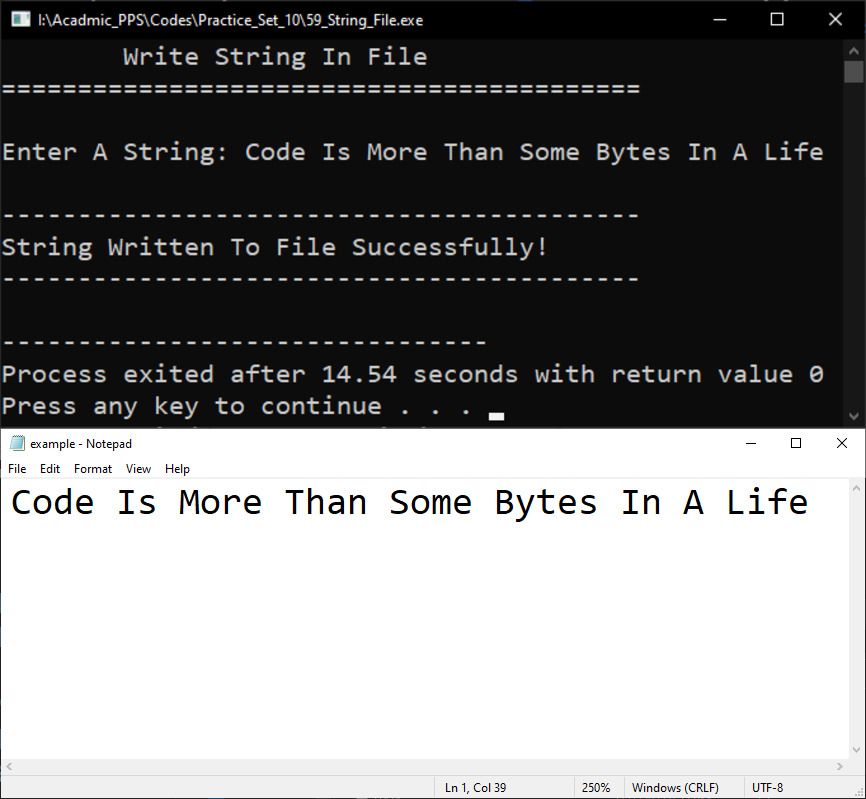
Output Image: